China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News. This article dives into China’s incredible manufacturing dominance, exploring its historical rise, key sectors, and the complex global implications. We’ll examine the infrastructure, workforce, and challenges facing this economic giant, offering a comprehensive overview of its manufacturing prowess and future prospects. Get ready for a fascinating journey into the heart of global production!
From humble beginnings, China strategically developed its manufacturing sector through targeted policies and economic reforms. This led to a dramatic increase in global market share across numerous industries, surpassing even established manufacturing powerhouses like Japan and Germany. We’ll analyze the factors behind this success, comparing China’s approach to infrastructure development and workforce management with other nations.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – a lot of those products probably use AI-generated voiceovers in their marketing. If you’re curious about the tech behind that, check out this helpful guide on comparing different AI voice generator software options to see how those voices are made. It’s fascinating to consider how even the seemingly simple aspects of global trade are increasingly reliant on advanced tech.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance

China’s rise as the world’s manufacturing powerhouse is a remarkable story of economic transformation, fueled by strategic policy decisions, massive infrastructure investments, and a vast, adaptable workforce. This dominance, however, isn’t without its challenges and implications for the global economy and geopolitical landscape.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: Historical Context
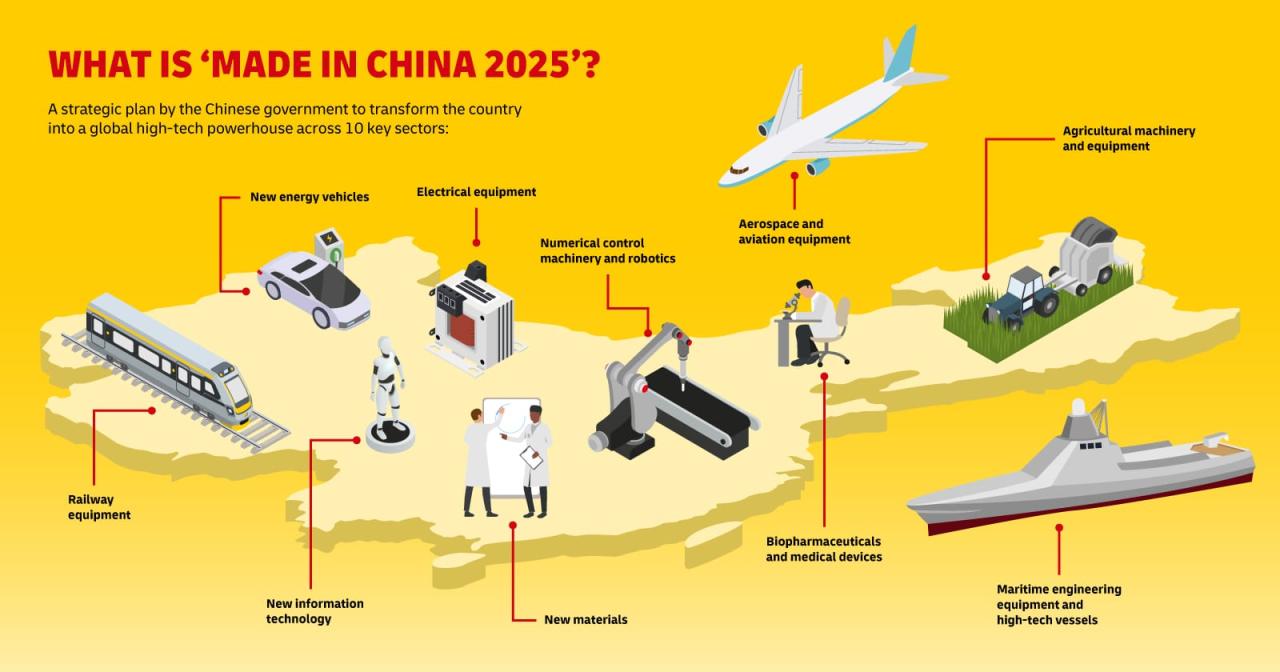
China’s journey to manufacturing supremacy began with gradual economic reforms in the late 1970s, shifting from a centrally planned economy to a more market-oriented system. The opening up to foreign investment, coupled with a focus on export-oriented industries, proved transformative. Key policy decisions like the establishment of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) attracted significant foreign direct investment (FDI), fostering technological transfer and expertise.
This contrasts sharply with the more gradual industrialization of Japan and Germany, which focused on domestic markets initially, and the US, which leveraged its abundant natural resources and technological innovation.
| Country | Year of Significant Growth | Key Industries | GDP Contribution from Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | 1980s-Present | Electronics, Textiles, Automobiles, Machinery, Steel | ~30% (varies yearly) |
| Japan | 1950s-1970s | Automobiles, Electronics, Shipbuilding | ~20-25% (historical average) |
| Germany | Post-WWII | Automobiles, Machinery, Chemicals | ~20-25% (historical average) |
| US | 19th-20th Centuries | Automobiles, Aerospace, Pharmaceuticals | ~10-15% (current) |
Key Sectors Driving China’s Manufacturing Power
Several key sectors propel China’s manufacturing might. Electronics, textiles, and automobiles are particularly prominent, boasting significant global market share. Technological advancements in these sectors, often driven by both domestic and foreign investment, are crucial. Companies like Huawei (telecommunications), BYD (automobiles), and Foxconn (electronics) exemplify China’s global manufacturing leadership, influencing global supply chains and technological trends.
Infrastructure and Supply Chains
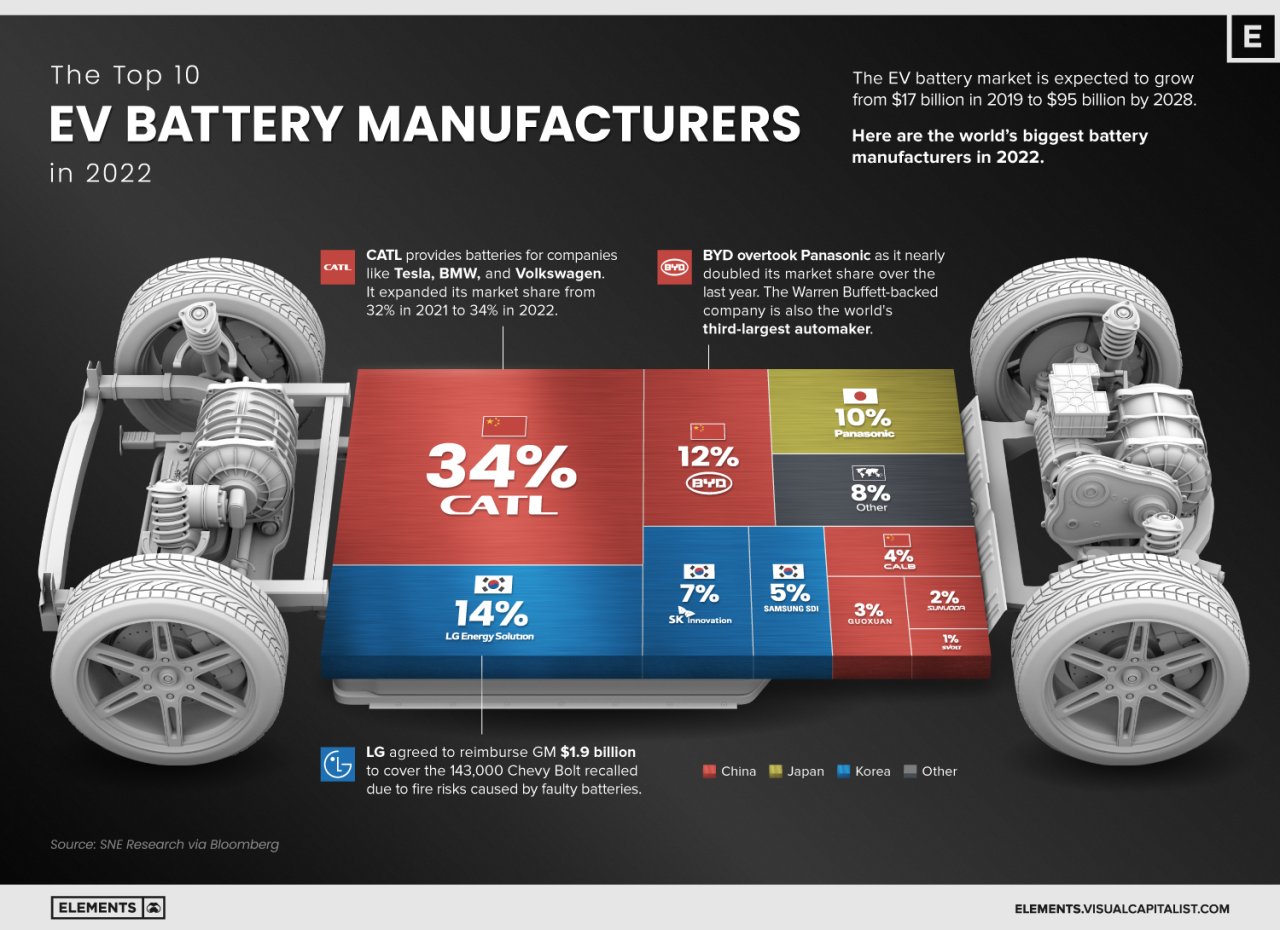
China’s extensive infrastructure network, including its vast port system, high-speed rail network, and expanding energy grid, plays a critical role in supporting its manufacturing capabilities. This infrastructure enables efficient movement of goods and resources, crucial for the seamless functioning of its global supply chains. However, the concentration of manufacturing in certain regions creates vulnerabilities, as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic.
China’s approach to infrastructure development, characterized by large-scale, state-led projects, differs from the more market-driven approaches of some other nations.
So, you’re reading about China’s manufacturing dominance on Hacker News? It’s a fascinating topic, especially when you consider the global impact. Think about how many products we use daily are made in China; it’s mind-boggling. This global reach is a stark contrast to, say, the focused ambition of the Nipissing Lakers women’s hockey team has high hopes for the upcoming season.
Their dedication, though on a smaller scale, mirrors the intense drive behind China’s manufacturing superpower status. It makes you appreciate the diverse scales of ambition around the world.
- China: Centrally planned, large-scale projects, rapid expansion.
- US: More market-driven, decentralized infrastructure development, slower pace of expansion.
- Germany: Strong focus on efficiency and technological integration, robust private sector involvement.
Labor and Workforce Dynamics, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News
China’s manufacturing workforce is characterized by its sheer size and historically low labor costs. While skill levels have improved significantly, the workforce remains a mix of skilled and unskilled labor. Automation and robotics are increasingly impacting employment, leading to job displacement in some sectors but also creating new opportunities in areas like robotics maintenance and software development. The social and economic implications of these shifts are complex, requiring policies to manage transitions and ensure social safety nets.
Challenges and Future Prospects
China’s manufacturing sector faces significant challenges, including rising labor costs, increasing environmental concerns, and intensifying technological competition. The future of Chinese manufacturing hinges on its ability to adapt to these challenges. A potential scenario involves a shift towards higher-value manufacturing, driven by technological innovation and a focus on sustainability. This could lead to a reduction in low-cost manufacturing and a reshaping of global supply chains.
Global Implications of China’s Manufacturing Hegemony

China’s manufacturing dominance significantly impacts global trade, economic growth, and geopolitical dynamics. Its influence extends across various sectors, shaping global supply chains and influencing economic policies worldwide.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – their factories probably churn out tons of basketballs, too! Speaking of which, check out the Lakers’ blowout win against the Hawks; you can read all about it in this game recap: Lakers 119-102 Hawks (Jan 3, 2025) Game Recap – ESPN. Anyway, back to China’s manufacturing might – it’s truly something else.
| Economic Impact | Geopolitical Impact | Social Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Increased global trade, lower consumer prices, economic interdependence | Shift in global power dynamics, increased competition for resources, potential for trade disputes | Job creation and displacement in different countries, changes in working conditions and labor standards |
Illustrative Example: The Electronics Manufacturing Sector in China
China’s electronics manufacturing sector, encompassing everything from smartphones to computers, is a prime example of its manufacturing prowess. The production process is highly complex, involving numerous stages.
Raw material sourcing (e.g., rare earth minerals) is often globally dispersed.
Component manufacturing (e.g., semiconductors, screens) involves intricate assembly lines, often involving foreign and domestic companies.
Final assembly and packaging involve high-volume production in massive factories.
Distribution and logistics utilize extensive networks, connecting factories to global markets.
A typical electronics factory in China is a large, multi-story building, often located in industrial parks. Inside, rows upon rows of assembly lines are filled with workers performing highly specialized tasks. Automated machinery is increasingly integrated into the production process, but human labor remains crucial for many stages. The factory environment is characterized by a structured and regimented workflow, with a strong emphasis on efficiency and output.
Final Conclusion: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News
China’s manufacturing dominance is undeniably a defining feature of the 21st-century global economy. While challenges remain, including rising labor costs and environmental concerns, China’s adaptability and technological advancements suggest a continued significant role in global manufacturing for the foreseeable future. Understanding this landscape is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike, as the implications ripple across global trade, geopolitics, and social structures.
The future of manufacturing, it seems, is inextricably linked to China’s continued evolution.
FAQ Guide
What are some of the biggest environmental concerns related to China’s manufacturing sector?
Air and water pollution from factories, waste disposal, and resource depletion are major environmental concerns. China is actively working to address these issues but faces significant hurdles.
How does China’s manufacturing sector impact developing countries?
It provides manufacturing jobs and investment opportunities, but also presents challenges related to competition and potential exploitation of labor in some cases.
What role does automation play in China’s manufacturing future?
Automation is rapidly increasing, aiming to improve efficiency and address rising labor costs, but also potentially displacing workers.
What are the ethical implications of China’s manufacturing dominance?
Concerns exist regarding worker rights, environmental responsibility, and the potential for unfair trade practices. Transparency and ethical sourcing are increasingly important considerations.
